Ehime University Research Unit
Ehime University established the Research Unit (RU) system in 2015 to further strengthen its research functions. This system is designed to further promote and invigorate research activities by recognizing research groups with outstanding achievements in distinctive and advanced research fields and with potential for future development.
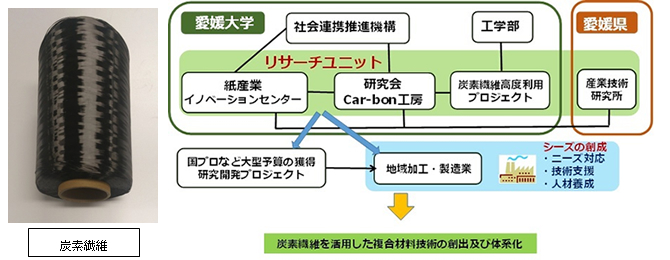
Carbon Fiber Composite Materials Research Unit
FY 2015 – FY 2017
Against the backdrop of Ehime Prefecture’s unique regional industry, which has a world-class manufacturing and development base for carbon fibers, this research unit was established for the following purposes
- The center will form an academic research center for the development of innovative composite materials (carbon fiber composites) using “carbon fibers”.
- We will contribute to local industries through industrial application of the developed carbon fiber composite materials.
- We will foster highly skilled technical personnel in the region by promoting joint research with Ehime Prefecture and local companies.
The center is consistent with Ehime University’s goal of “strengthening and expanding regional cooperation and industry-government-academia collaboration, and promoting human resource development and academic research that contributes to regional revitalization,” and aims to be a center that appeals to people in Japan and abroad as a distinctive research center of Ehime University.
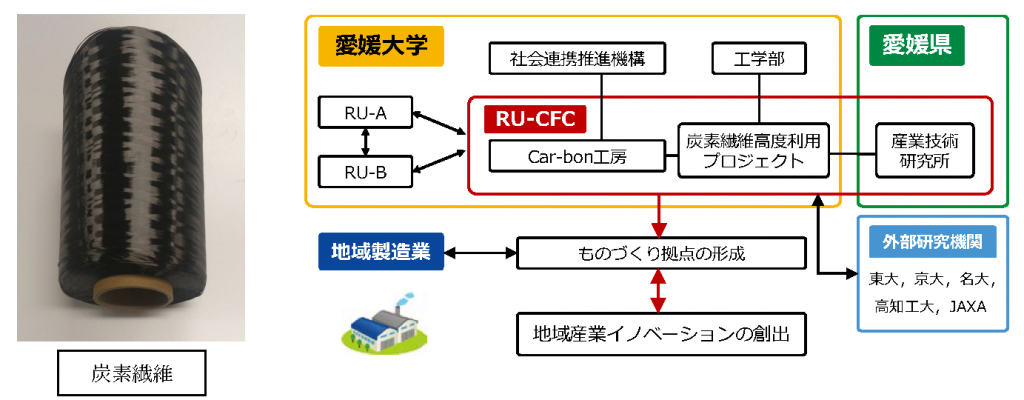
Fiscal year 2008 – 2020
The Research Unit was established in Ehime Prefecture, which has a world-class manufacturing and development base for carbon fibers, with the following objectives
- The center will form an academic research center for the development of innovative composite materials (carbon fiber composites) using “carbon fibers”.
- We will contribute to local industries by applying the developed carbon fiber composite materials to industrial applications.
- We promote joint research with Ehime Prefecture and local companies to foster highly skilled technical personnel in the region.
- We will strengthen collaboration among RUs within the university and form the seeds of a manufacturing center that can contribute to the local community.
The center is in line with Ehime University’s goal of “strengthening functions to create regional industrial innovation,” and aims to be a center that appeals both domestically and internationally as a distinctive research center of Ehime University.
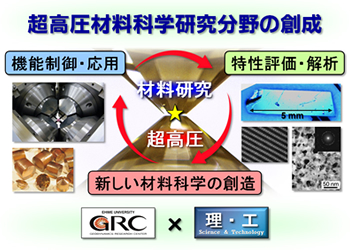
High Pressure Materials Science Unit
Ehime University is a world-class center for high-pressure science with the world’s leading ultrahigh-pressure generators, and the world of ultrahigh pressure exceeding 100,000 atmospheres is an unknown world where materials with completely different properties from those we see in our daily lives exist. The Unit aims to contribute to the formation of a better society by conducting materials science research under ultrahigh pressure and developing new materials that can solve social issues such as energy conservation and effective use of resources.
The Unit is an interdisciplinary research organization consisting of researchers working in different fields such as physics, electronic materials, metallic materials, organic chemistry, and geoscience. The Unit aims to create a world-leading center for materials science in Ehime, Japan, through collaboration of the knowledge and networks of each researcher.
The accreditation period of this RU has expired and the RU will be active as a new research division of the Research Center for Deep Earth Dynamics, “High Pressure Materials Science Division” starting from the fiscal year 2008.
The results of the RU ex-post evaluation showed that the original objectives had been achieved and the period of accreditation had expired in a developed form, and in addition, the University was recognized as implementing noteworthy initiatives, and the University was given a certificate of accreditation. Advanced Research Unit (ARU) Based on the support program, we have decided to provide partial support for activity expenses.
Glocal Area Studies Unit
Fiscal year 2008~2010
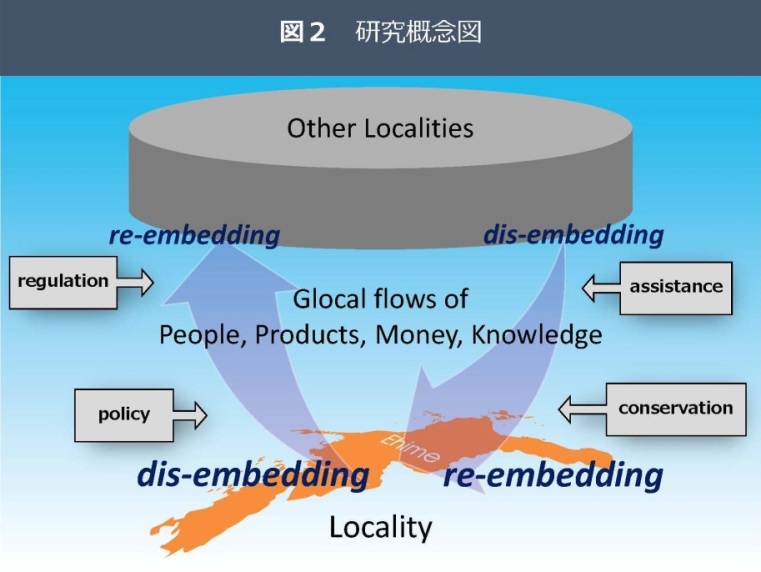
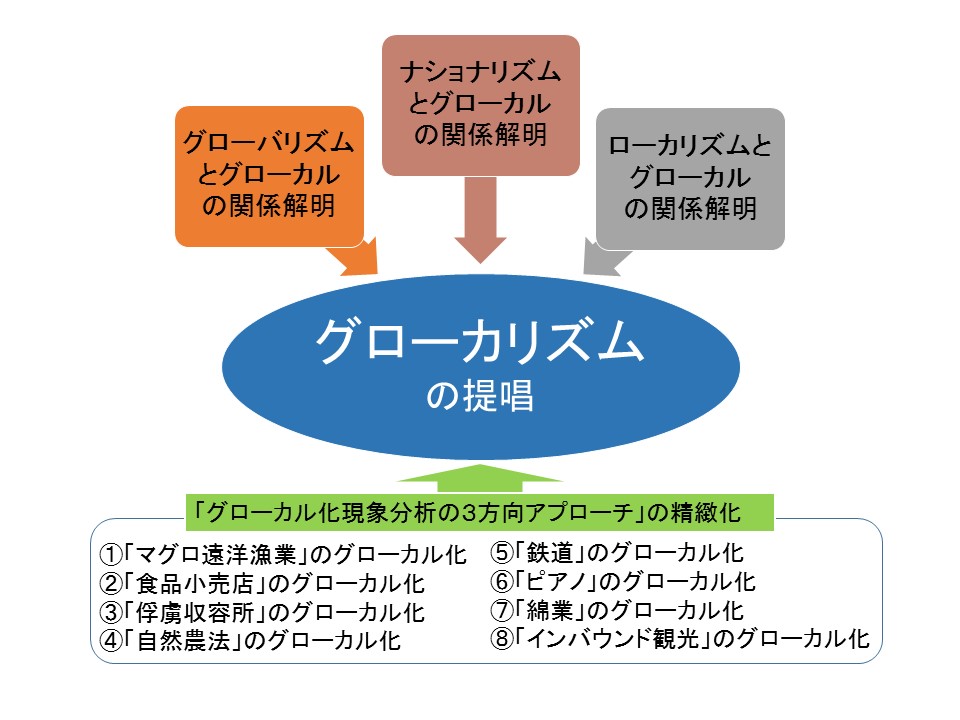
This unit analyzes the process by which values, technologies, and institutions cultivated locally spread and take root in various parts of the world, aiming to build Ehime University’s own “Global Studies” and “Glocal Area Studies,” and to effectively link research with education.
Through three case studies, “Seattle Uwajimaya Study,” “Masanobu Fukuoka and Natural Farming Study,” and “Transboundary Sea Nomad Study,” we will explore the dynamics of glocal movement of people, goods, and money and “de-embedding => re-embedding.
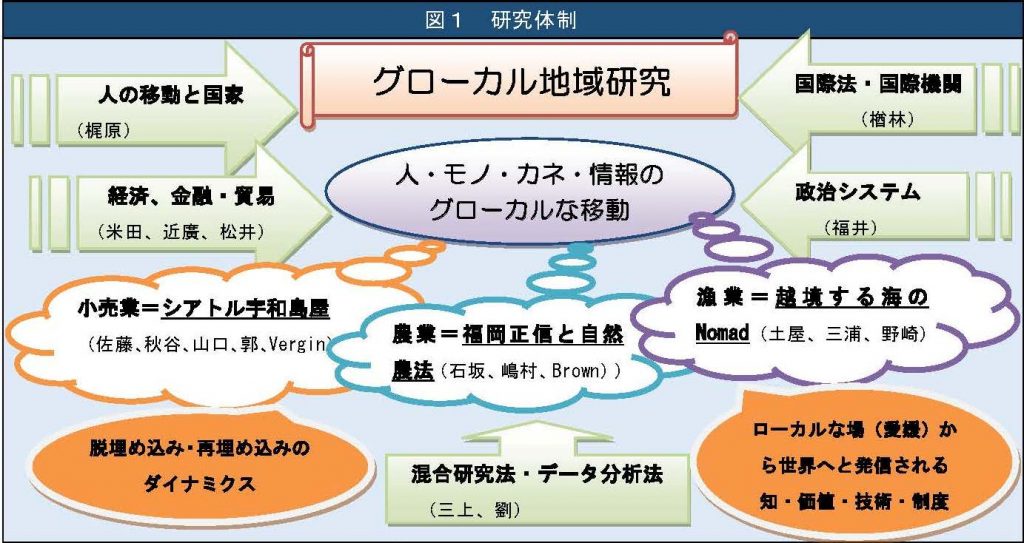
2021 – 2021
We will construct a framework and methodology to academically understand and analyze the dynamic process by which knowledge, values, technologies, and institutions cultivated in local places spread and take root in various parts of the world with the movement of people, goods, money, and information, and contribute to the formation of “glocal area studies” as a new academic field.
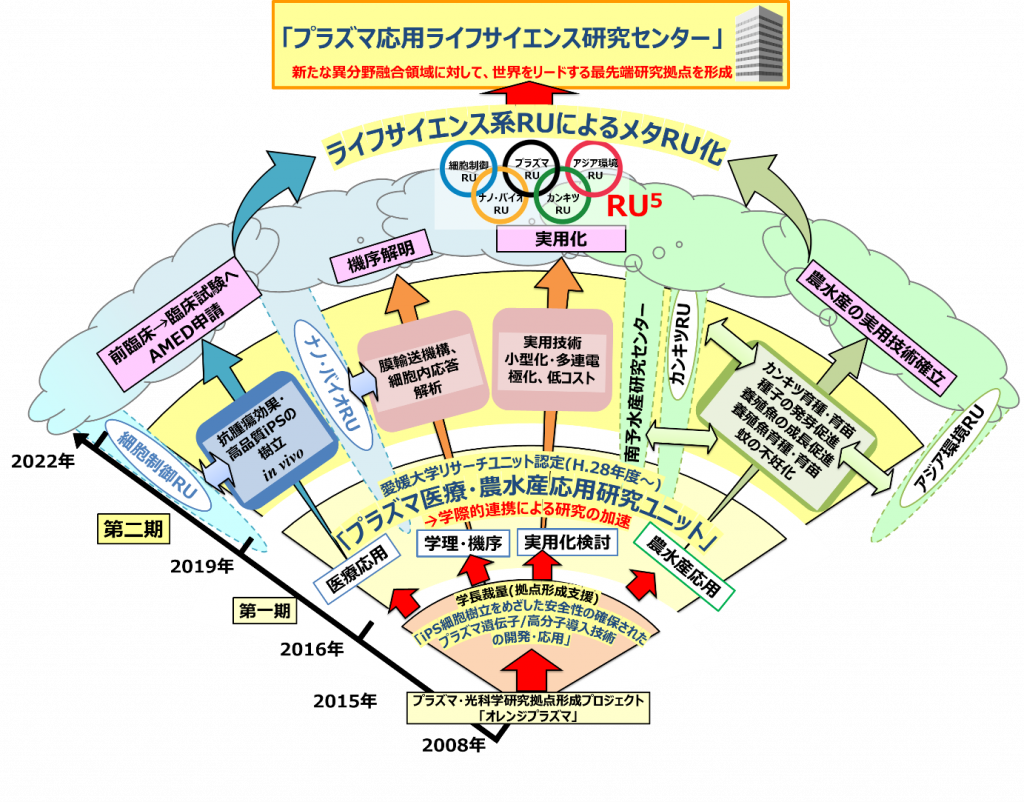
Plasma Medicine, Agriculture and Fisheries Application Research Unit
Fiscal year 2008~2010
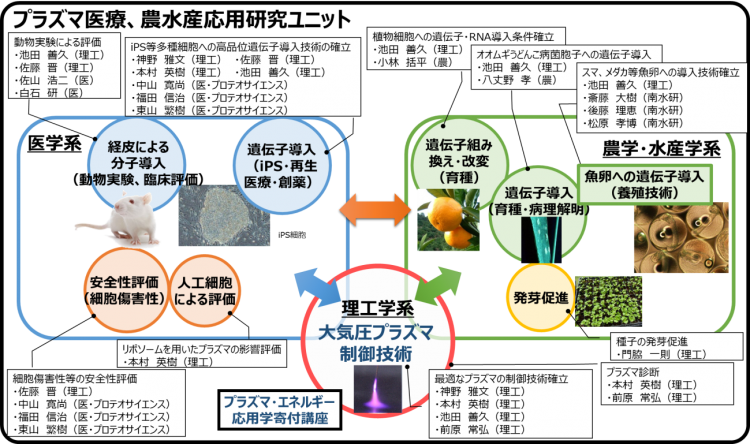
This Research Unit is an extension of the results of the “Development and Application of Plasma Gene/Polymer Introduction Technology,” which was adopted as a Center Formation Support Research Activation Project of Ehime University from 2013 to 2015, with the addition of new collaborations with the Faculty of Agriculture and the Nanyo Fisheries Research Center.
(1) Advancement of research in the medical, agricultural, and fishery fields through practical application of plasma gene/molecule transfer technology
(2) Accelerate interdisciplinary research by creating new academic fields based on interdisciplinary cooperation and obtaining external funding
The main objective of the project is to
2021 – 2021
This Research Unit (RU) will expand on the results of the “Development and application of safe plasma gene/macromolecule transfection technology for the establishment of iPS cells,” which was selected as Ehime University’s Center Formation Support Research Activation Project from FY2013 to FY2015, and will work on (1) the development of large-scale external collaboration through a broad cross-disciplinary cooperation system, and (2) the development and application of plasma gene/ macromolecule transfection technology for the establishment of iPS cells. (2) to promote interdisciplinary research and the practical application of technology in medicine, science, engineering and agriculture, and (3) to lay the groundwork for the formation of a world-leading cutting-edge research center through a new fusion of different fields by providing plasma technology and promoting collaboration among life science-related RUs. The project is to promote
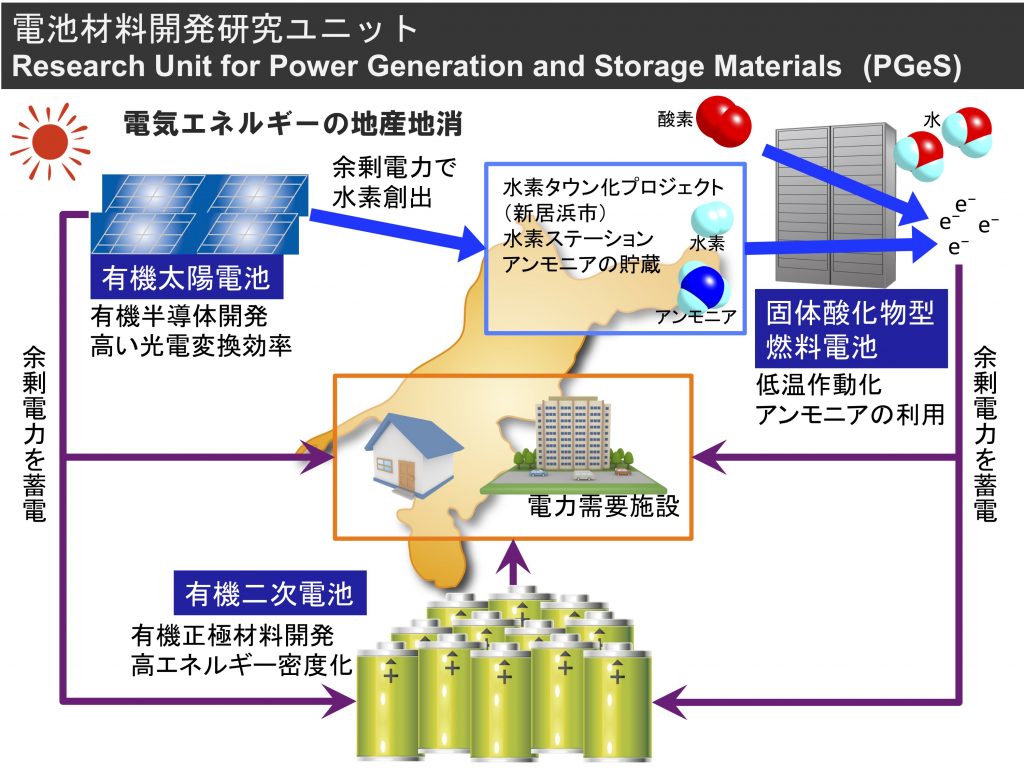
Battery Materials Development Research Unit
Fiscal year 2008~2010
This research unit aims to develop innovative materials and technologies that contribute to improving the performance of fuel cells and solar cells, which are responsible for the generation of electrical energy (Power Generation), and rechargeable batteries, which are responsible for the storage of electrical energy (Power Storage).
By bringing together researchers involved in different types of batteries, we will work toward solving the global warming problems currently facing the world as a whole, and toward the realization of a low-carbon society and a sustainable smart society through research and development of semiconductor materials for solid oxide fuel cells and organic solar cells and cathode materials for organic rechargeable batteries.
2021 – 2021
The objective of this research unit is to develop innovative materials and technologies that contribute to improving the performance of fuel cells and solar cells, which are responsible for the generation of electrical energy (Power Generation), and rechargeable batteries, which are responsible for the storage of electrical energy (Power Storage).
By bringing together researchers involved in different types of batteries, we will work toward solving the global warming problems currently facing the world as a whole, and toward the realization of a low-carbon society and a sustainable smart society through research and development of semiconductor materials for solid oxide fuel cells and organic solar cells and cathode materials for organic rechargeable batteries.
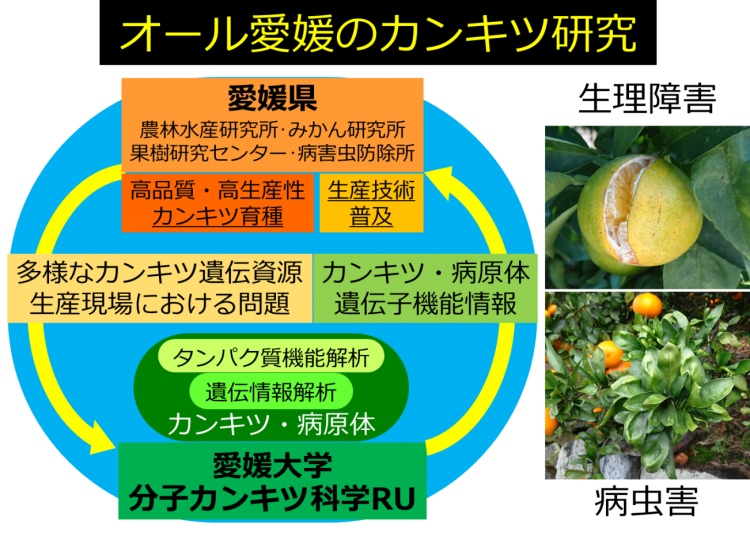
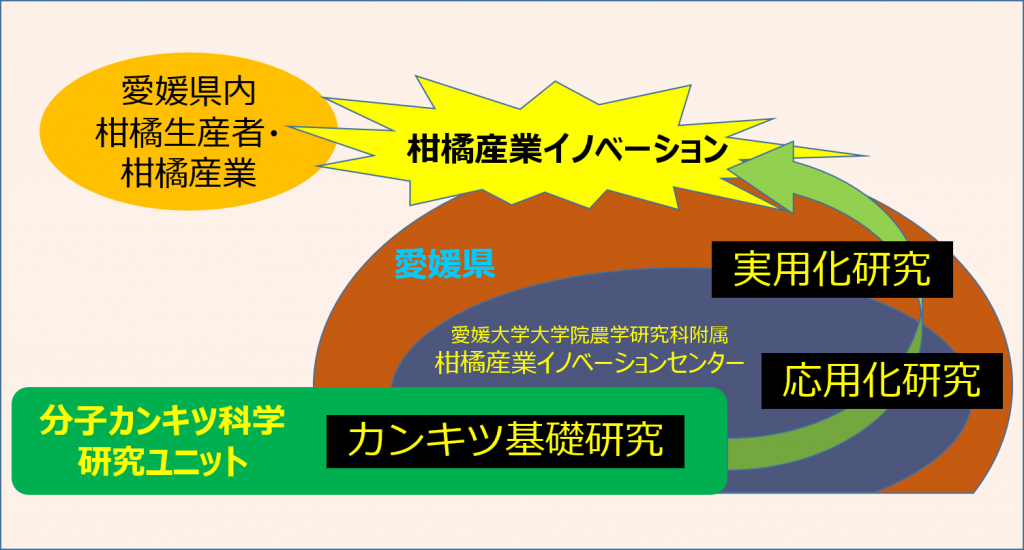
Molecular Cankerworm Science Unit
Fiscal year 2008~2010
At Ehime University, which aims to be “a university that moves the region and connects with the world with its shining individuality,” this research unit will form the basis for research on genes and proteins to overcome pests and physiological disorders by utilizing the genetic resources of the citrus plant owned by Ehime Prefecture.
The “All Ehime Kumquat Research” project, which shares this research platform with research institutions in Ehime Prefecture, will contribute to solving various problems in Kumquat production in Ehime Prefecture and around the world through the breeding of superior varieties and the development of pest control chemicals.
2021 – 2021
In Ehime University, which aims to be “a university that moves the region and connects with the world with its shining individuality,” the Research Unit has been conducting genetic research since its establishment in 2016 with the goal of developing high value-added varieties, overcoming pest and physiological disorders, etc., focusing on the citrus genetic resources of Ehime Prefecture. In close collaboration with the Citrus Industry Innovation Center affiliated with the Graduate School of Agricultural Science and research institutions in Ehime Prefecture, we will return the results of our research to society and contribute to the development of Ehime’s citrus industry through further basic research.
Organic Superconductors Research Unit
Fiscal Year 2009~2028
This unit aims to elucidate the mechanism of the phenomenon of superconductivity using organic materials as an example, and to develop superior superconductors. Superconductivity occurs only at very low temperatures, such as -70°C to -270°C. However, if superconductivity can be achieved even at room temperature (around 20°C), dream-like technologies such as power transmission without any energy loss and railroads connecting Tokyo and Nagoya in 40 minutes will become a reality. Our dream is to spread the “industrial revolution caused by superconductivity” from Ehime University to the world by advancing this kind of research.
From 2020 to 2022
This unit aims to elucidate the mechanism of the phenomenon of superconductivity using organic materials as an example, and to develop superior superconductors. Superconductivity occurs only at very low temperatures (-70°C to -270°C) and under very high pressure (1.5 GPa). However, if superconductivity can be achieved even at normal temperatures and pressures (1 atmospheric pressure, around 20°C), dream-like technologies such as power transmission with no energy loss and a railroad connecting Tokyo and Nagoya in 40 minutes will become a reality. Our dream is to spread the “industrial revolution caused by superconductivity” from Ehime University to the world by advancing this kind of research.

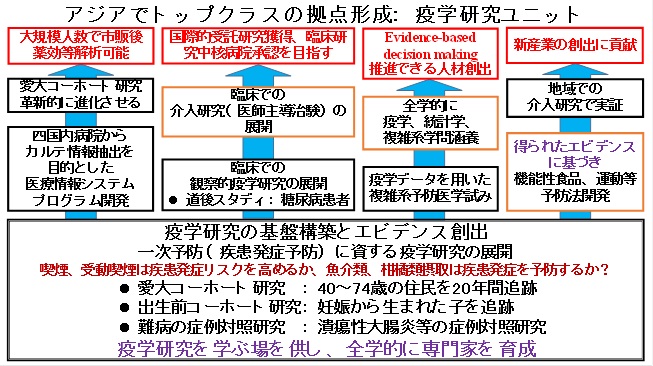
Formation of a top-class center in Asia: Epidemiology Research Unit
Fiscal Year 2009~2028
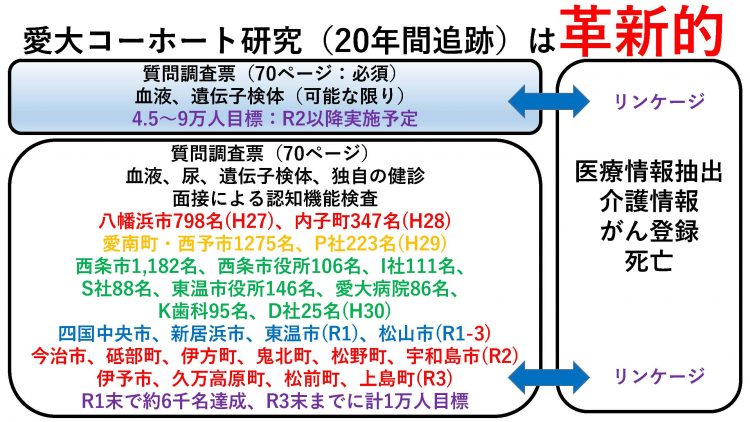
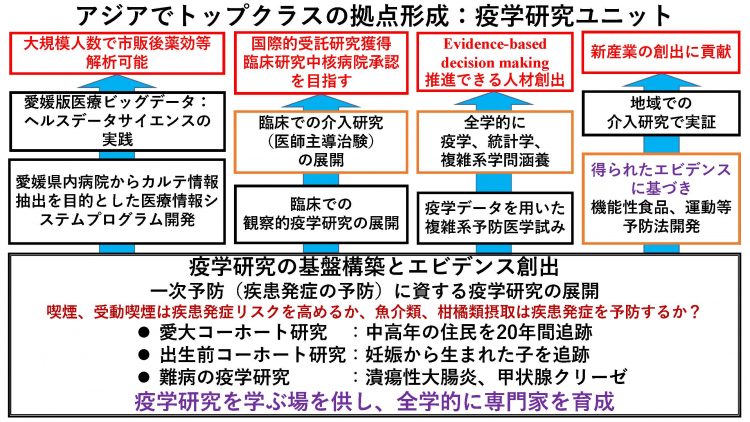
With the “Ai-Dai Cohort Study” targeting middle-aged and older adults as the core, we will generate numerous evidences that contribute to primary prevention (prevention of disease onset) through prenatal cohort studies and case-control studies of intractable diseases. We will also develop a system to extract electronic medical record information from medical institutions and collate epidemiological data with medical information derived from electronic medical records to innovatively advance the “Aioi University Cohort Study”. We will provide a place to study epidemiology on a university-wide basis. Furthermore, we will accelerate the application of epidemiology to clinical observational epidemiological research and intervention research, and contribute to the development of human resources capable of promoting evidence-based decision making and the creation of new industries through medical-agricultural collaboration.
From 2020 to 2022
With the “AIDA University Cohort Study” targeting middle-aged and older adults as the core, we will generate numerous evidences that contribute to primary prevention (prevention of disease onset) through prenatal cohort studies targeting mothers and children and epidemiological studies of intractable diseases. We will also develop a system to extract electronic medical record information from medical institutions to promote health data science on a county-wide basis. Separately, we will collate epidemiological data with medical information derived from electronic medical records to innovatively advance the “Aioi University Cohort Study. We will provide a place to study epidemiology on a university-wide basis. Furthermore, we will accelerate the application of epidemiology to clinical observational epidemiological research and intervention research, and contribute to the development of human resources capable of promoting evidence-based decision making and the creation of new industries through medical-agricultural collaboration.
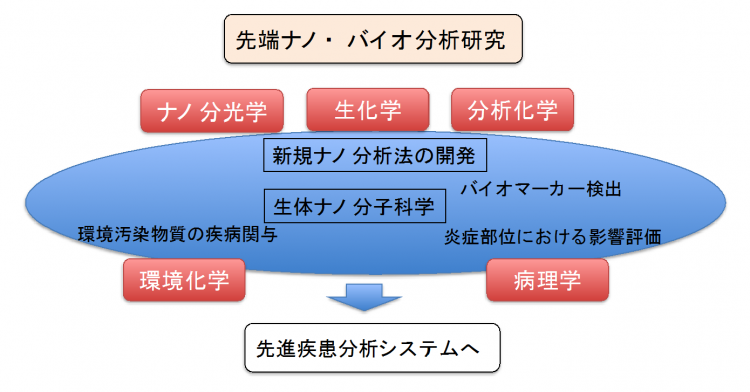
Advanced Nano-Bioanalysis Research Unit
The objective of this research unit is to develop advanced bioanalytical techniques for highly selective and sensitive detection of target causative agents by combining bioanalysis using nanoparticles and spectroscopic analysis. Furthermore, this technique will be applied to medical/medical applications and environmental science applications. In particular, we aim at early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and other diseases by detecting trace amounts of causative substances. We also aim to construct an advanced analytical system for highly sensitive detection of environmental pollutants and their relationship to diseases.
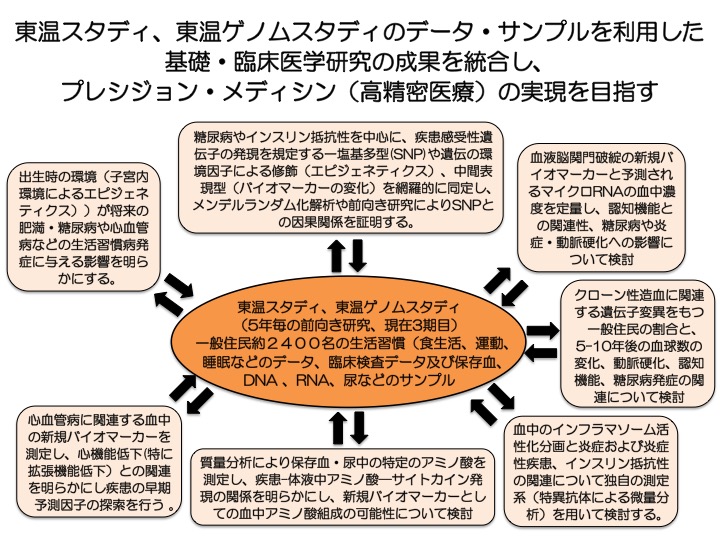
High Precision Medicine and Translational Research Unit
In this RU, basic and clinical medical researchers will collaborate and use clinical data and samples obtained from the Tohon Genome Study of the general population to examine (1) gene polymorphisms (SNPs) and modifications by environmental factors (epigenetics) associated with the development of diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and dementia, (2) the role of SNPs in predicting disease onset, and (3) the role of SNPs in predicting disease onset in the general population. The project aims to establish a method to predict disease onset by identifying biomarkers and microRNAs, 3) adding lifestyle and environmental factor data to (1) and (2) and analyzing these data in an integrated manner, and to realize precision medicine for preventive medicine.
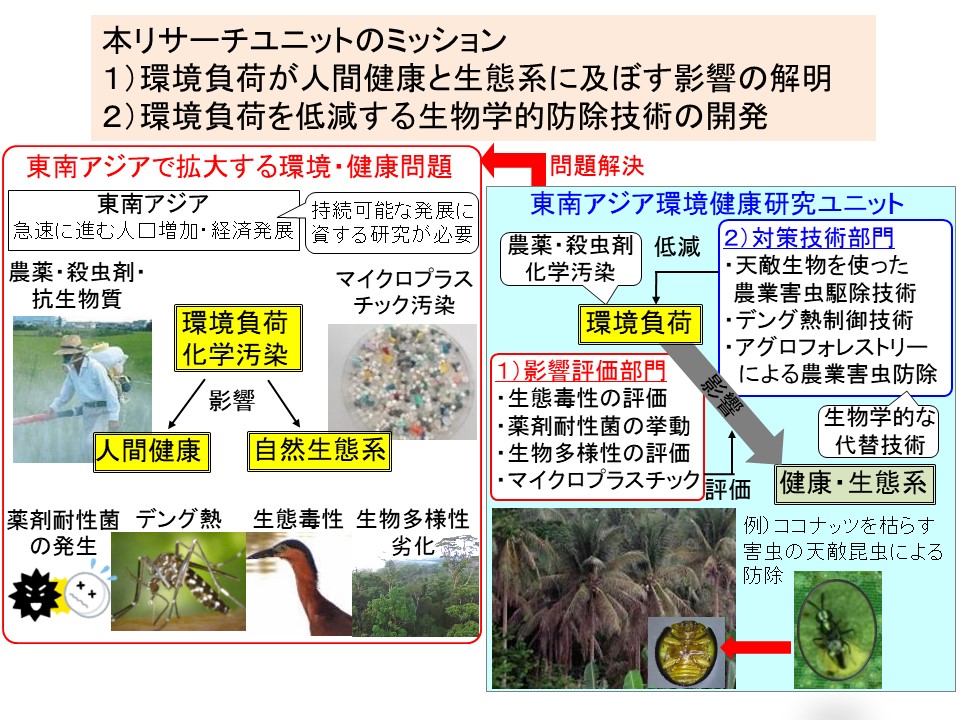
Southeast Asia Environmental Health Research Unit
In Southeast Asia, where economic development is rapidly advancing, excessive use of pesticides and chemical pollution such as insecticides used for infectious disease-carrying mosquitoes is widespread. This RU will bring together research groups within the university whose keywords are “Southeast Asia,” “environment,” and “health” to form an international research center that will contribute to solving environmental and health problems in Southeast Asia. This RU consists of 1) Impact Assessment Division and 2) Countermeasure Technology Division. These two divisions are in charge of 1) impact assessment of environmental impacts on human health and natural ecosystems, and 2) development of biological control technologies to mitigate these environmental impacts.
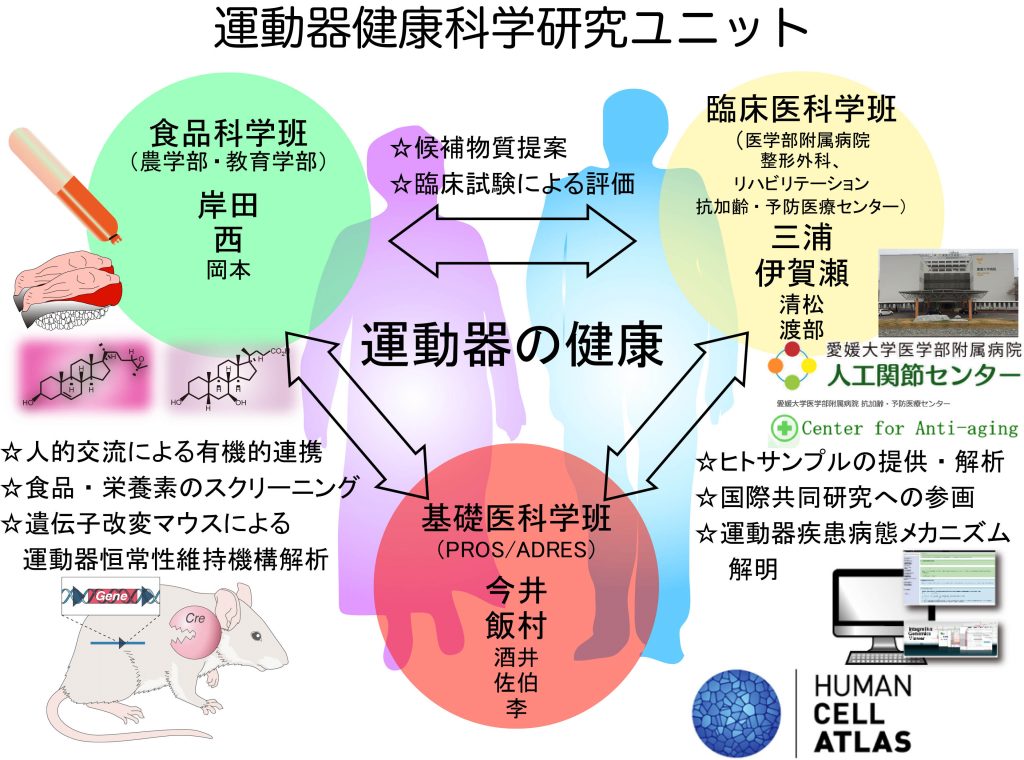
Research Unit for Motor Health Science
As Japan enters a hyper-aged society, the realization of a healthy and long-lived society has become a social issue that must be overcome. With locomotor diseases accounting for more than 1/3 of the factors for requiring assistance, it is essential to take measures against locomotor diseases (locomotive syndrome). Against this background, food science, locomotive clinical medicine, and basic medical science are collaborating in various ways to analyze the functions of foods and nutrients to clarify their mechanisms of action. Furthermore, by conducting clinical research, we will contribute to actual health promotion focusing on maintenance, disease prevention, and recovery of the locomotor system, and challenge the acquisition of healthy longevity.
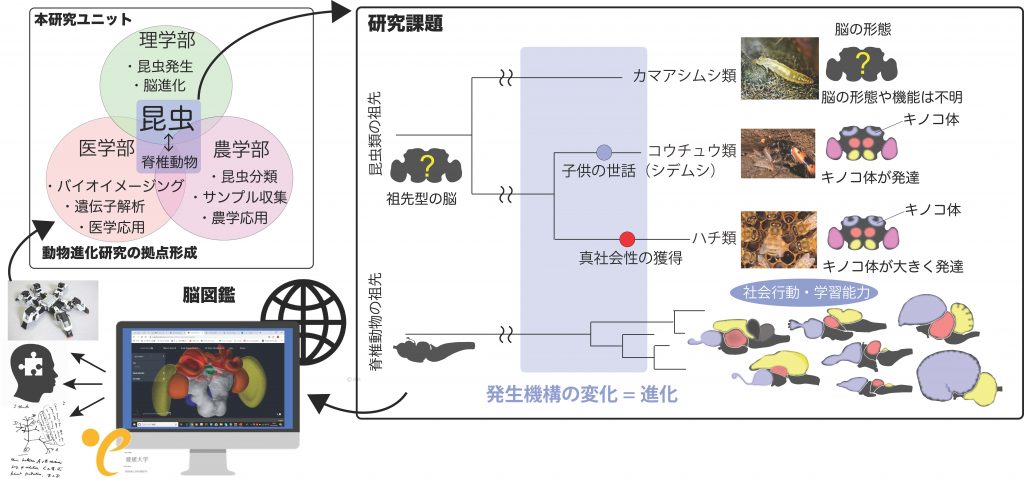
Research Unit for Brain Evolution Revealed from Insects
In this RU, researchers from three science departments (Faculty of Science, Faculty of Medicine, and Faculty of Agriculture) will collaborate to apply advanced molecular development and imaging techniques to the “brain” of insects, the largest group of animals, in order to elucidate the process of brain evolution. Furthermore, by comparing them with vertebrates of higher intelligence, we will explore the factors that have made these two groups the champions of the earth. We will also create and publish a 3D atlas database of brain development, the “Brain Atlas,” to form an electronic research center for animal evolution and promote collaborative research with other fields for the further development of the RU. The project will lead to the following
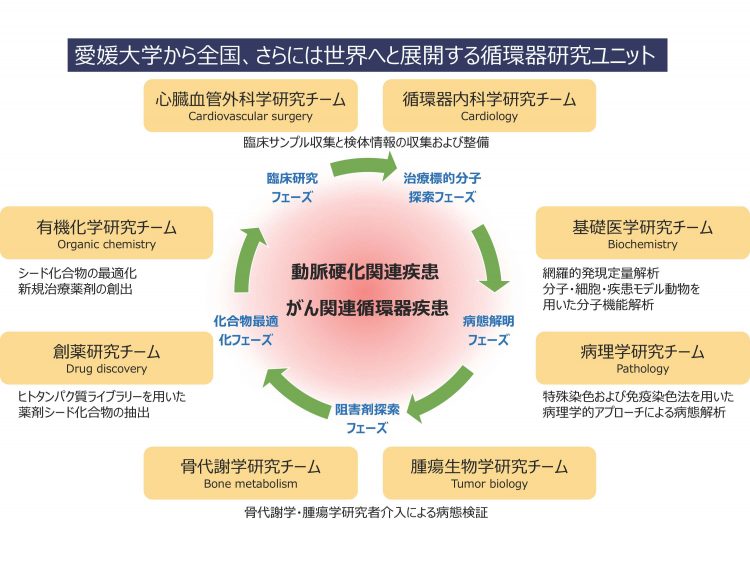
Cardiovascular Research Unit to link clinical specimens to drug discovery
This research unit aims to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of (1) atherosclerosis-related diseases and (2) next-generation cardiovascular diseases linked to cancer therapy, both from Ehime University. Researchers in pathology/cardiovascular medicine/cardiovascular surgery/vascular biology/tumor biology/bone metabolism/organic chemistry/protein engineering, respectively, will operate a research cycle from molecule-cell-tissue-individual-drug discovery to clinical application starting from clinical specimens, aiming to create novel therapeutic and preventive methods never seen before.